UOP690, C₈ and Low Boiling Paraffins and Naphthenes in Low-Olefin Hydrocarbons by GC
INTRODUCTION
The UOP690 describes the determination method for C8 and lower boiling paraffins and naphthenes in olefin free gasolines (2 mass-%) with a maximum boiling point of 260°C. In this method benzene and toluene are also being determined.
This method contains two procedures using the same column to determine the resolved non-aromatic components. Depending on the degree of resolution required either method A alone, or both method A and B can be used. Method A looks at a broad spectrum of components while method B zooms in on the lighter components and this data can be used to calculate unresolved non-aromatic components from method A.
Figure 1 shows the SCION Instruments 4X6 GC platforms that can be used for UOP690.


EXPERIMENTAL
This analysis can be implemented on the 436-GC and the 456-GC platform. The analysis was performed on the Scion 456-GC analyser equipped with an FID and a 100 positions 8400 autosampler. The conditions for each method can be found in Table 1 and Table 2.
Table 1. Analytical conditions of method A
| Injector | Splitless 200:1, 250 °C |
| Column | SCION-DHA-50 |
| Oven Program | 32°C (6.0 min), 5°C/min to 52°C (14.0 min) , 20 °C/min to 250°C (9 min) |
| Carrier | Hydrogen, 1.1 ml/min ( *GC equipped with a H2 sensor bundle) |
| Detector | FID with ceramic jet, 250°C Air: 300 ml/min, Fuel gas (H2): 30 ml/min, Make up (N2): 30 ml/min |
| Inj. Volume | 0.5 µl |
| Autosampler | 8400 |
| Software | Compass CDS |
Table 2. Analytical conditions of method B
| Injector | Splitless 200:1, 250 °C |
| Column | SCION-DHA-50 |
| Oven Program | 60°C (8.0 min), 5°C/min to 90°C (0 min) , 20 °C/min to 250°C (10 min) |
| Carrier | Hydrogen, 1.1 ml/min ( *GC equipped with a H2 sensor bundle) |
| Detector | FID with ceramic jet, 250°C Air: 300 ml/min, Fuel gas (H2): 30 ml/min, Make up (N2): 30 ml/min |
| Inj. Volume | 0.5 µl |
| Autosampler | 8400 |
| Software | Compass CDS |
The UOP 690 is a perfect and simple method for the determination of the mass-% composition of the sample.
A big advantage of running both methods is the possibility for detailed identification by comparing chromatograms of method A and B. With these methods it is possible to determine the unresolved non-aromatic components from method A.
In Table 3, the components that have to be determined by analysis A and B can be found.
Table 3: Components determined with analysis A and B, peak number with letters refer to co-eluting peaks.
| Peak Nr. A | Peak Nr. B | Component | Peak Nr. A | Peak Nr. B | Component |
| 1 | – | Propane | 36 | – | 3.3-Dimethylhexane |
| 2 | – | Isobutane | 37 | – | 1-trans-2-cis-3-Trimethylcyclopentane |
| 3 | – | n-Butane | 38 | – | 2.3.4-Trimethylpentane |
| 4 | – | 2.2-Dimethylpropane | 39A | – | 2.3.3-Trimethylpentane |
| 5 | – | Isopentane | 39B | – | Toluene |
| 6 | – | n-Pentane | 40A | 6 | 2.3-Dimethylhexane |
| 7 | – | 2.2-Dimethylbutane | 40B | 7 | 1.1.2-Trimethylcyclopentane |
| 8 | – | Cyclopentane | 41 | – | 2-Methyl-3-ethylpentane |
| 9 | – | 2.3-Dimethylbutane | 42 | – | 2-Methylheptane |
| 10 | – | 2-Methylpentane | 43 | – | 4-Methylheptane |
| 11 | – | 3-Methylpentane | 44A | – | 3.4-Dimethylhexane |
| 12 | – | n-Hexane | 44B | – | 3-Methyl-3-ethylpentane |
| 13 | – | 2.2-Dimethylpentane | 45A | – | 1-cis-2-trans-4-Trimethylcyclopentane |
| 14 | – | Methylcyclopentane | 45B | 8B | 1-cis-2-cis-4-Trimethylcyclopentane |
| 15 | – | 2.4-Dimethylpentane | 46 | – | 3-Methylheptane |
| 16 | – | 2.2.3-Trimethylbutane | 47A | 8A | 3-Ethylhexane |
| 17 | – | Benzene | 47B | 9A | 1-cis-3-Dimethylcyclohexane |
| 18 | – | 3.3-Dimethylpentane | 47C | 9B | 1-cis-2-trans-3-Trimethylcyclopentane |
| 19 | – | Cyclohexane | 48 | – | 1-trans-4-Dimethylcyclohexane |
| 20 | – | 2-Methylhexane | 49 | – | 1.1-Dimethylcyclohexane |
| 21 | – | 2.3-Dimethylpentane | 50 | – | 1-Methyl-trans-3-ethylcyclopentane |
| 22 | – | 1.1-Dimethylcyclopentane | 51 | – | 1-Methyl-cis-2-ethylcyclopentane |
| 23 | – | 3-Methylhexane | 52 | – | 1-Methyl-trans-2-ethylcyclopentane |
| 24 | – | 1-cis-3-Dimethylcyclopentane | 53 | – | 1-Methyl-1-ethylcyclopentane |
| 25 | – | 1-trans-3-Dimethylcyclopentane | 54 | – | 1-trans-2-Dimethylcyclohexane |
| 26 | – | 3-Ethylpentane | 55 | – | 1-cis-2-cis-3-Trimethylcyclopentane |
| 27 | – | 1-trans-2-Dimethylcyclopentane | 56A | 10 | n-Octane |
| 28 | – | 2.2.4-Trimethylpentane | 56B | 11 | 1-cis-4-Dimethylcyclohexane |
| 29 | – | n-Heptane | 56C | 12 | 1-trans-3-Dimethylcyclohexane |
| 30A | 2 | Methylcyclohexane | 57 | – | Isopropylcyclopentane |
| 30B | 1A | 1-cis-2-Dimethylcyclopentane | 58 | – | 1-Methyl-cis-2-ethylcyclopentane |
| 31A | 3 | 1.1.3-Trimethhylcyclopentane | 59 | – | 1-cis-2-Dimethylcyclohexane |
| 31B | 1B | 2.2-Dimethylhexane | 60A | 13 | n-Propylcyclohexane |
| 32 | 4A | Ethylcyclopentane | 60B | 14 | Ethylcyclohexane |
| 33 | 2.5-Dimethylhexane | 61 | – | Ethylbenzene | |
| 34A | 5 | 2.2.3-Trimethylpentane | 62A | – | m-Xylene |
| 34B | 4B | 2.4-Dimethylhexane | 62B | – | p-Xylene |
| 35 | – | 1-trans-2-cis-4-Trimethylcyclopentane | 63 | – | o-Xylene |
RESULTS
All the results were calculated according to the described method in UOP690.
The theoretical relative response factors (TRRF) were determined and showed a deviation from the theoretical value below 3% for the components.
In addition it showed that the three measurements performed for these components had a deviation below 1% amongst the results. These results were excellent since the deviation against the theoretical values have to be below 5% and the deviation amongst the results no more than 2%.
After establishing the TRRF a gasoline mix was injected to determine the mass-% . This gasoline mix was analysed with method A and method B.
Both methods showed excellent repeatability that are well withing specifications prescribed in the UOP 690.
After analysis and calculation of the mass it showed that the sum of all components (resolved and unresolved) was 99.63 mass-%, this means that the data had to be renormalized to 100 mass-%.
An example of the chromatograms from method A and B can be found in figure 2.
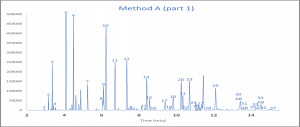
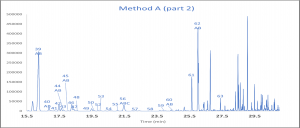
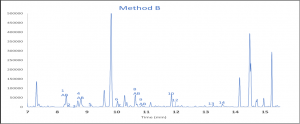
CONCLUSION
The Scion 4X6-GC analyser equipped with a split/spitless injector, Scion Instruments column and FID is capable of performing UOP690 in a way that complies to the method. The C8 and low boiling paraffins and naphthenes are determined on the basis of mass-%, The quantitation limit for any reported component is 0.01 mass-%. The equipment of the 4X6-GC analyser is pre determined, for ordering information or customisation, please contact your local sales representative.
Download Application Note: UOP960, C8 and Low Boiling Paraffins and Naphthenes in Low-olefin Hydrcarbons by GC
Download complete Application Note: UOP690, C₈ and low boiling paraffins and naphthenes in low-olefin hydrocarbons by GC
Keep in Touch
If you wish to speak to a member of our team about more information, please don’t hesitate to contact us. Or if you wish to keep up to date with SCION Instruments latest research and articles, join us on social media and sign up to our newsletters today.
