Blood Alcohol Determination By Versa Headspace Sampling
Introduction
Blood alcohol analysis is one of a variety of headspace methods performed in forensic toxicology laboratories. The Versa was evaluated to determine its suitability to perform an occasional blood alcohol test. Methanol, acetone, ethanol, isopropanol and acetaldehyde along with n-propanol, a typical internal standard, were tested with the Versa headspace instrument. These volatile organic compounds which must be accurately identified and quantified, especially in legal medical cases in which the compounds are contributing factors to death or criminal investigations.

Figure 1. SCION Instruments Versa Headspace Sampler
Experimental
The Versa headspace instrument was connected to GC with FID for this application note. A ZB-BAC-1 column, 30m x 0.53mm x 3.0µm was used to perform the quantitation portion of the analysis. Table 1 displays the Versa parameters for the blood alcohol analysis. Table 2 displays the GC/FID parameters used for the separation of the six blood alcohol components.
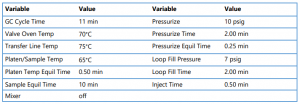
Table 1. Versa Loop Parameters

Table 2. GC/FID Method parameters
An internal standard solution was prepared by adding approximately 620µL of n-propanol into a 1L flask containing 20g of sodium chloride dissolved in deionized water. An accuracy test mix was prepared by adding approximately 90µL of acetaldehyde, 175µL of methanol, 70µL of acetone, 110µL of isopropanol and 105µL of ethanol into a 100mL volumetric flask containing deionized water. A set of 7 accuracy standards were prepared by adding 1mL of the internal standard and 0.5mL of the test mix into 22mL headspace vials. These were capped with Teflon lined septa and sealed. Blanks were prepared by placing 1mL of internal standard and 0.5mL of deionized water into 22mL headspace vials.
A linearity test mix was prepared by adding approximately 370µL of acetaldehyde, 690µL of methanol, 270µL of acetone, 430µL of isopropanol, and 420µL of ethanol into a 100mL volumetric flask containing deionized water. A linear standard series was prepared by pipetting 3µL, 10µL, 30µL, 60µL, 125µL, 250µL, and 500µL into separate 22mL headspace vials containing 1mL of internal standard solution. Water was added to the vials so that the total volume of test mix and water was equal to 1.5mL. These were sealed with Teflon-lined septa and sealed. Table 3 lists the concentrations of the accuracy and linearity standards in g/dL
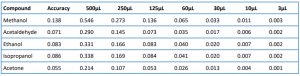
Table 3. Accuracy and Linearity Approximate Concentrations in g/dL for the 0.5mL Samples Added to 1mL of Internal Standard Solution
Results
The CDS software was used to measure the peak areas of all solvents from both the accuracy and the linearity study. The peak area data was entered into a Microsoft Excel spreadsheet. The average and the percent relative standard deviations (%RSD) were calculated from the accuracy samples by both external and internal standard methods. N-Propanol was used as the internal standard. This data is presented in Table 4.
The correlation coefficient (r2) was calculated from the linearity standards by both external and internal standard methods. This data is presented in Table 5.
The chromatogram of the standard is presented in Figure 2.
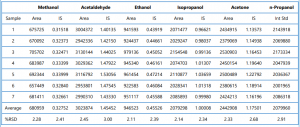
Table 4: Average and %RSD of Methanol, Acetaldehyde, Ethanol, Isopropanol, Acetone and n-Propanol of the 7 Accuracy Standards Calculated by External (Area) and Internal Standard (IS) Methods
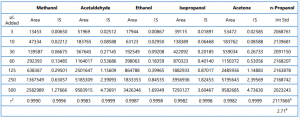
Table 5: Correlation Coefficient (r2) of the Seven Point Calibration Curve of Methanol, Acetaldehyde, Ethanol, Isopropanol, Acetone Calculated by External (Area) and Internal Standard (IS) Methods. The averageª and the %RSDᴮ are calculated for the internal standard, n-propanol.
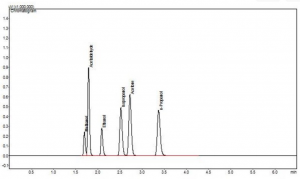
Figure 2. Chromatogram of the Blood Alcohol Standards
Conclusion
The Versa was tested with a typical blood alcohol method to determine the percent relative standard deviation (%RSD) of a set of 7 standards. The %RSD was less than 3% for the six typical blood alcohol solvents calculated by either the external or internal standard method.
A linearity study from 0.002g/dL to 0.33g/dL ethanol provided a correlation coefficient (r2) greater than 0.999 by either the external or internal standard calculation method. The other solvents had a correlation coefficient (r2) greater than 0.998 by either the external standard or internal standard calculation method for a similar concentration range.
Download Application Note
Download the complete Application Note: Blood Alcohol Determination By Versa Headspace Sampling
Keep in Touch
If you wish to speak to a member of our team about more information, please don’t hesitate to contact us. Or if you wish to keep up to date with SCION Instruments latest research and articles, why not join us on social media and sign up to our newsletters today?
