HPLC Troubleshooting Guide
Dive into our analyse troubleshooting comprehensive HPLC troubleshooting guide and resolve any issues with your analysis today.
Retention time drift
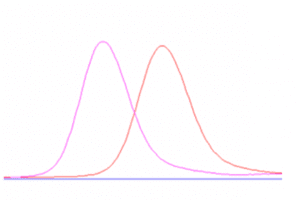
- Poor temperature control – Use thermostat column oven. Change column oven temperature.
- Incorrect mobile phase composition – Prepare fresh mobile phase. Check mixer is working for gradient methods.
- Poor column equilibration – Increase column equilibration time. Condition the column.
- Change in flow rate – Reset flow rate. Test using a liquid flow meter.
- Air bubbles in the system – Degas the mobile phase. Purge the system.
Baseline noise
- Leak – Check for loose fittings. Tighten gently. Check pump seals. Replace if worn out.
- Incorrect mobile phase – Check for the use of only miscible mobile phases and correct preparation.
- Air bubbles in system – Flush system with a strong organic solvent. Purge the system. Degas mobile phase.
- Detector cell contaminated – Clean cell flow.
- Detector lamp low energy – Replace lamp.
- Stationary phase of column exposed – Replace column.
Baseline drifting
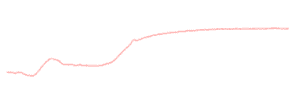
- Column temperature fluctuation – Use a thermostat column oven. Use a thermometer to check the accuracy of the set temperature.
- Incorrect mobile phase composition – Prepare fresh mobile phase. Check mixer is working for gradient methods.
- Contamination of detector flow cell – Flush flow cell with a strong organic solvent. If no improvement is seen, change the flow cell.
- Damaged flow cell – Replace flow cell.
- Pump outlet blocked – Remove blockage. If no improvement is seen, replace outlet.
- Flow rate change – Reset flow rate. Test using liquid flow meter.
- Poor column equilibration – Increase column equilibration time. If recently changed mobile phase, purge the system and pump of old solvent with new mobile phase using 20 column volumes.
- Retained peaks look like baseline drifts –Use a guard column. Thoroughly flush the column with a strong organic solvent before the next injection.
- UV detector not set at maximum absorbance – Use maximum absorbance wavelength of target compound(s)
- Reference wavelength of detector is incorrect – Ensure reference wavelength of the detector is different to target compounds.
- UV absorbing mobile phase – Use non-UV absorbing HPLC grade solvent.
Baseline pulsing

- Proportioning valves are sticking – Clean thoroughly. If necessary, replace valves (I am not quite sure what is meant by proportioning valves are sticking)
- Debris in the flow cell – Check flow cell and flush. If contaminated, contact SCION engineer for maintenance.
Broad peaks

- Mobile phase composition changed – Make new mobile phase. Add buffer to mobile phase.
- Leaks between column and detector – Check for loose fittings.
- Flow rate too low – Increase flow rate.
- Detector not set correctly – Check detector settings and adjust.
- Column overloading – Decrease injection volume.
- Tubing between column and detector is too long and/or incorrect internal diameter – Reduce flow path. Use narrower internal diameter tubing.
- Guard column/ column contaminated – Replace guard column/ column.
- No resolution of two peaks – Change column to improve separation.
- Column temperature too low – Increase column temperature.
Peak tailing
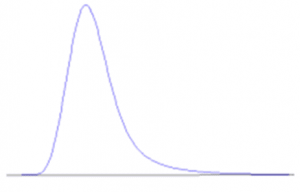
- Flow path too long – Use narrower and shorter PEEK tubing.
- Prolonged analyte retention – Modify mobile phase composition. Use appropriate mobile phase buffer. Use a different stationary phase column.
- Blocked column – Reverse phase flush column with a strong organic solvent. Replace column.
- Interfering peak – Change mobile phase composition. Increase gradient program. Use longer column.
- Wrong mobile phase pH – Adjust mobile phase pH. Prepare new mobile phase with correct pH.
- Active sites on column – Change column.
Extra peaks
- Contamination – Flush system with a strong organic solvent. Use/replace guard column, filter sample and replace filters in solvent bottle.
- Carry over – Flush system with a strong organic solvent. Increase run time or gradient.
- Ghost peaks – Prepare fresh mobile phase. Reduce injection volume.
Peak fronting

- Column temperature too low – Increase temperature. Use thermostat column over.
- Sample overload – Reduce injection volume. Dilute sample
- Wrong mobile phase composition – Prepare fresh mobile phase.
- Solvent incompatibility – Prepare/dilute sample in the mobile phase.
- Column stationary phase depleted – Replace column. Use new column with different stationary phase.
Peak Distortion
- Injection – Reduce injection volume. Dilute sample. Use weaker injection solvent.
- Ghost peaks – Decrease injection volume. Prepare fresh mobile phase.
- Carry over – Flush system with a strong organic solvent. Increase run time and gradient.
Split peaks
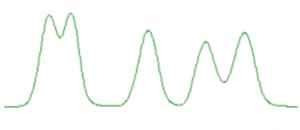
- Contamination – Flush system with a strong organic solvent. Use/replace guard column, filter sample and replace filters in solvent bottle.
- Wrong mobile phase composition – Prepare fresh mobile phase. Change mobile phase to suit target compound(s).
Loss of sensitivity

- Injection volume too low – Check injection volume is correct.
- Needle blocked – Flush needle. Replace needle.
- Detector time constant too large – Decrease time constant.
- Contaminated guard column/ column – Replace guard column/ column.
- Incorrect mobile phase composition – Prepare new mobile phase.
- Air bubbles in system – Degas the mobile phase. Purge the system.
Low resolution
- Contaminated mobile phase – Prepare new mobile phase.
- Contaminated guard column/ column – Replace guard column/ column.
Pressure fluctuations
- Air in system – Degas all solvents. Purge pump.
- Check valve fault – Replace check valves.
- Leak – Identify leak. Tighten/replace fittings.
- Pump seal failure – Replace seal.
- Blocked flow cell – Clean flow cell. Replace flow cell.
- Blocked column – Reverse flush column, if possible. Replace guard column and/or column.
- Blocked injector – Flush needle and tubing. Replace the needle and/or tubing.
- Blocked pump – Flush with strong solvent. Change in-line filter.
No pressure
- Power supply off – Turn on power supply. Check/replace fuse.
- Piston damage – Replace piston.
- Air bubbles in the system – Purge system. Prime system with mobile phase.
- No mobile phase – Prepare new mobile phase.
- Check valves fault – Check valves. Replace valves.
- Leak – Identify source of the leak. Tighten fittings. Replace fittings.
High pressure
- Flow rate too high – Lower flow rate.
- Column blockage – Backflush column. Replace column.
- Injector blockage – Flush injector with a strong organic solvent. Replace injector.
- Column temperature too low – Increase column temperature.
- Mobile phase precipitation – Flush the system with a strong organic solvent. Prepare fresh mobile phase.
- In-liner filter blockage – Replace filter.
Low pressure
- Flow rate too low – Increase flow rate.
- Leak – Identify leak. Tighten fittings. Replace fittings.
- Column temperature too high – Decrease column temperature.
General leaks
- Fittings are loose, overtightened or damaged – Check all fittings. Loosen or tighten. Replace damaged fittings.
- Incompatible parts – Ensure all tubing and fittings are compatible. Replace with appropriate fittings.
Leaks at pump and autosampler
- Seal failure – Check all seals. Replace with new.
- Sample loop blocked – Flush with a strong organic solvent. Replace sample loop.
- Waste tubing blocked – Flush with a strong organic solvent. Replace waste tubing.
- Syringe failure – Tighten syringe gently. Replace syringe.
Leaks at column
- End-fittings are loose – Tighten gently.
- Wrong sized frit thickness. Use correct frit.
- Tubing installed incorrectly – Replace all tubing with correct size.
Leaks at detector
- Flow cell damaged – Replace flow cell.
- Flow cell blocked – Flush flow cell with solvent.
- Loose fittings – Tighten all fittings gently.
Get In Touch
If you have any questions regarding HPLC troubleshooting, get in touch.

