Analysis of Flavour Compounds in Milk Flavourings
Introduction
Dairy based milk powders offer a healthy alternative to fresh milk whilst also being readily available to incorporate into milk flavoured products during manufacturing. Whilst consumers expect highly soluble and great tasting products, manufacturers need reliable high quality instrumentation for determining the right chemical composition of their products.
Gas chromatography is the most commonly used chromatography technique for analysing food products, especially milk powders, for the identification of aroma compounds. The identification of the aroma compounds is vital as they constitute the taste and smell of all food products.Solid Phase Micro Extraction (SPME) is a solid phase extraction technique that involves the use of a fiber coated in a polymer or sorbent extracting phase. The fiber is exposed to a sample where sample analytes are absorbed onto the fiber coating. The fiber coating should be chosen to suit the type of analyte in the sample. During injection into the GC inlet, desorption occurs and the analytes are introduced to the analytical system. The quantity of analyte extracted by the fiber is proportional to its concentration in the sample as long as equilibrium is reached.
Experimental
A SCION 456 GC and SCION single quad (SQ) mass spectrometer (MS) equipped with 8400 autosampler, operated in SPME mode, was used to analyse both a milk powder and liquid sample containing milk flavours. The liquid sample was prepared by dissolving milk powder into propylene glycol. The milk powder is the basis to most food products containing milky flavours. Table 1 details the analytical conditions of the GC-MS with SPME autosampler.
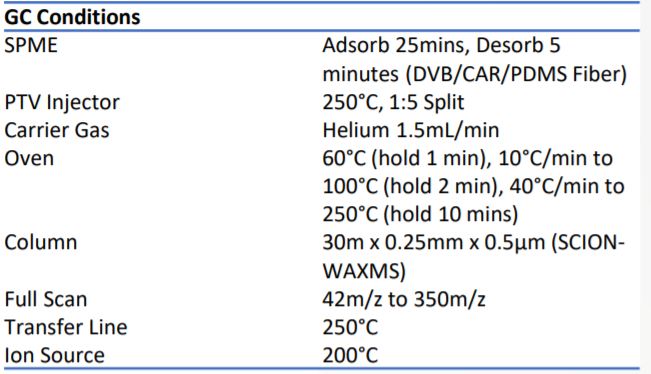
Table 1. Analytical conditions of the GC-MS with SPME
150mg of the liquid sample and 150mg of the milk powder were independently weight into 2mL vials along with 150mg of high grade water. Samples were heated at 30°C for 30 minutes prior to being exposed to the SPME fiber.
Results
Mass Spec Work Station is the software used to control the SCION GC-MS and data processing. NIST is an inbuilt mass
spectral library which was used to identify the flavour compounds in both the liquid and powder samples. Figures 1 and 2 detail the chromatograms obtained when both liquid and powder sample was analysed by SPME-GC-MS. Tables 2 and 3 detail the flavour compounds identified in the liquid and powder samples by NIST.
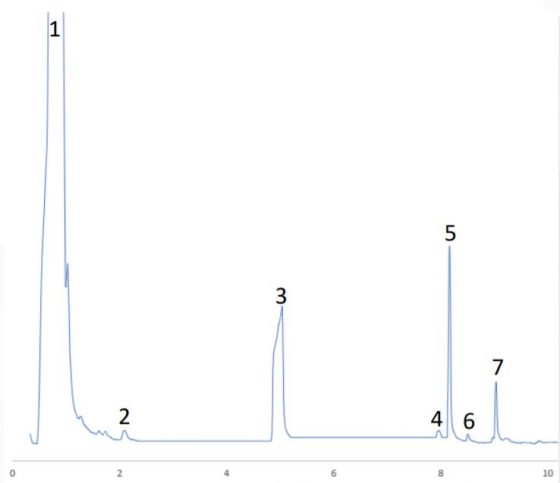
Fig 1. MS chromatogram of liquid sample
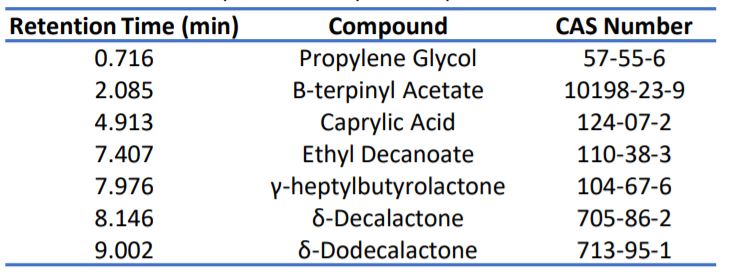
Table 2. Flavour compounds of liquid sample.
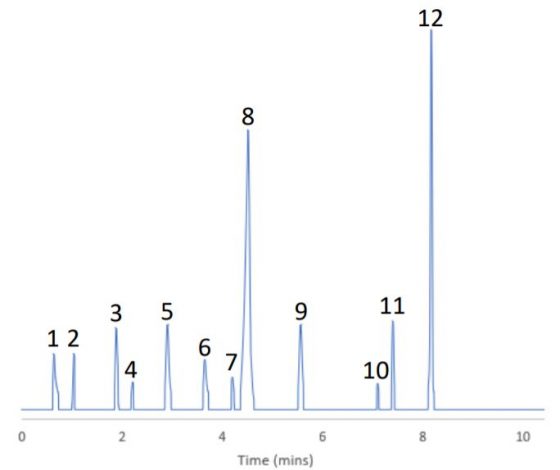
Fig 2. MS chromatogram of powder sample
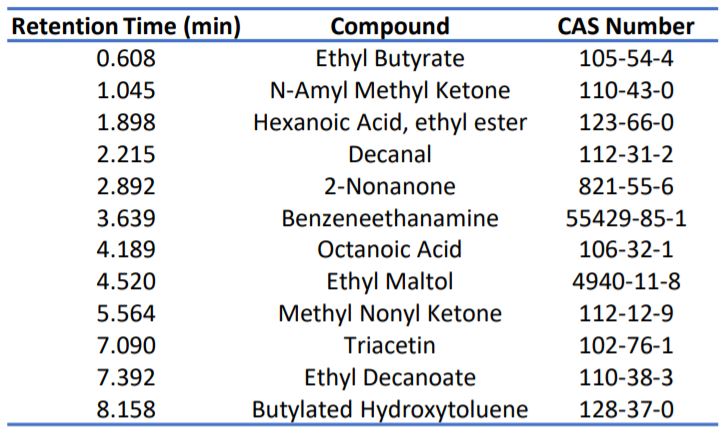
Table 3. Flavour compounds of powder sample.
Repeatability testing of both liquid and powder sample was performed using six replicates of each sample using SPME-GC-MS. Tables 4 and 5 detail the repeatability of both samples.
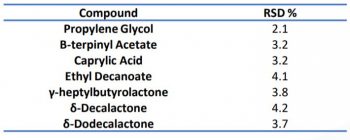
Table 4. Liquid sample repeatability (n=6)
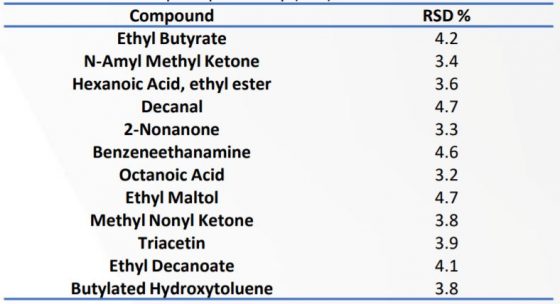
Table 5. Powder sample repeatability (n=6).
Conclusion
The SCION 456 GC with MS and automated SPME was used to identify flavour compounds commonly found in milk based products. Both liquid and powered samples containing milk flavourings were analysed with peak identification confirmed via NIST spectra library comparisons. Excellent repeatability was achieved, highlighting the robustness of the SCION SPME autosampler and GC-MS system.
Download Application Note
Download the complete Application Note: Analysis of Flavour Compounds in Milk Flavourings
SCION Gas Chromatography Analyser
A SCION Gas Chromatography Analyser was used to conduct this research. Providing excellent solutions for Environmental, Oil and Gas and Chemical industries, find out more about Scion GC Analysers.
If you would like to speak to a member of our team for more information, please don’t hesitate to get in touch. Or to stay in the loop regarding future research and articles from SCION Instruments, why not join us on social media and sign up to our eNewsletter today?
