Ammonia synthesis - Case Study
Ammonia synthesis – Catalytic Applications with Gas Chromatography
Ammonia synthesis, discovered by Fritz Haber and Carl Bosch in the early 20th century, revolutionized agricultural productivity and industrial chemistry. The process involves the reaction of nitrogen (N2) and hydrogen (H2) over an iron-based catalyst at high temperature and pressure conditions. Continuous monitoring of ammonia synthesis is crucial for maintaining optimal reaction conditions, maximizing yield, and minimizing energy consumption. Gas Chromatography has emerged as a versatile analytical technique for real-time analysis of reaction products and by-products, offering insights into catalyst performance and process efficiency.
Online Analysis in Ammonia Synthesis
Gas Chromatography can be used for online analysis to continuously monitor the concentrations of ammonia, nitrogen, hydrogen, and potentially other gas-phase species such as nitrogen oxides (NOx) and methane (CH4). Samples are typically withdrawn from the reactor effluent at regular intervals using an automated sampling system and injected into the GC system for separation and detection. Advanced techniques like GC coupled with mass spectrometry (GC-MS) may be employed for enhanced specificity and identification of trace components.
Applications and Benefits
Real-time Monitoring:
• Enables continuous measurement of reaction kinetics and product distributions, facilitating immediate adjustments to reaction conditions for optimal performance.
Quantitative Analysis:
• Provides accurate quantification of ammonia yield, nitrogen conversion, and hydrogen utilization efficiency, essential for process optimization.
Catalyst Evaluation:
• Evaluates catalyst activity, selectivity, and stability under dynamic reaction conditions, aiding in the development of robust catalyst systems.
Process Control:
• Facilitates fine-tuning of operational parameters such as temperature, pressure, and feed composition to maximize ammonia production while minimizing environmental impact.
Customer Case Example
In the following example, SCION Instruments worked with our customer to provide a Gas Chromatography based analytical tool for online analysis during ammonia synthesis, offering real-time insights into reaction kinetics, product distribution, and catalyst performance.
By leveraging the SCION GC’s capabilities, it is possible to optimize catalyst design, improve reaction efficiency, and advance sustainable practices in ammonia production.
Method
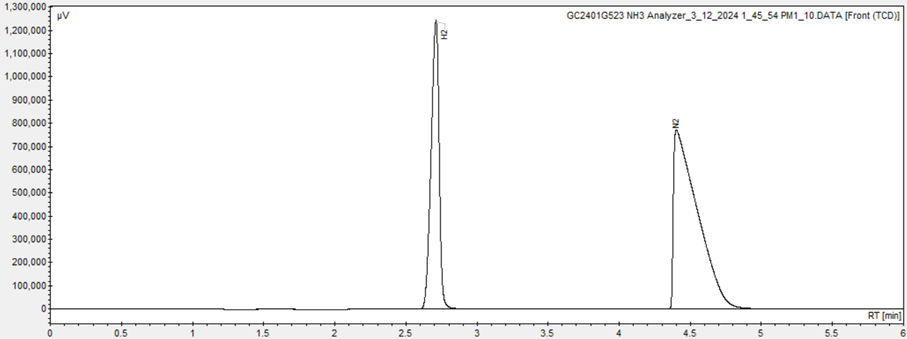
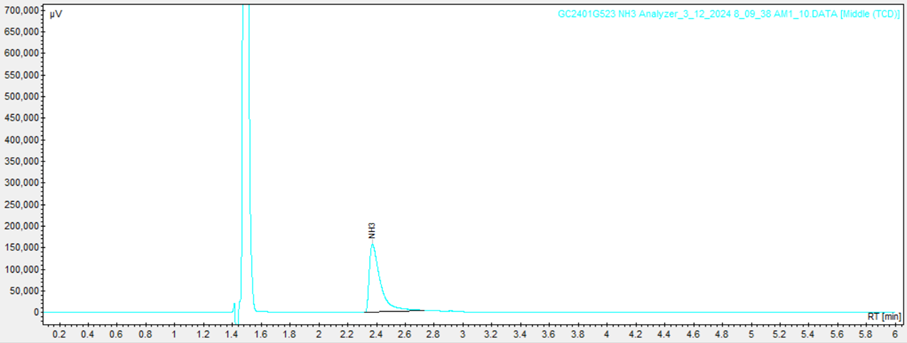
The SCION GC is used to perform online analysis of the ammonia synthesis. The quantification of H2, N2 will be done on a first TCD and ammonia on a second TCD.
The results obtained from the SCION GC analysis provide the total areas of each constituent. These total areas serve as quantitative measures of the amounts of each compound produced during the reaction.
By comparing the total areas of the starting material (N2 and H2) with those of the desired product (NH3) and any undesired by-products, they can calculate subsequently the conversion, selectivity, and turnover frequency of the reaction.
These calculations provide valuable insights into the efficiency and performance of the catalyst system, allowing for optimization and improvement of the reaction conditions to enhance product yield and selectivity.
System Configuration
Ammonia Synthesis:
SCION 8500-GC 2 channels
1st channel : GSV, two columns Molsieve 5A & Hayesep Q and TCD à H2 & N2 determination
2nd channel : GSV, column Hayesep Q and TCD à NH3 determination
Software : CompassCDS
Whether you are a researcher, a process engineer, or an industry professional, you will gain valuable knowledge to advance your understanding and application of catalysts using gas chromatography. Take a look at our additional case studies:
Toluene hydrogenation – Case Study
CO2 methanation – Case Study
Propane Aromatization – Case Study
Toluene Methanolation – Case Study